Update: After version 7 CUBA was renamed to Jmix, which is effectively 8th major version of the platform.
It has been a year and several important releases since CUBA Platform was presented to the international developers community, so in this article I would like to provide an updated overview, explaining what value it brings to enterprise software developers.
Readers will learn:
- What is CUBA Platform and its architecture?
- What types of solutions CUBA Platform is most efficient at?
- How does the platform cut development time?
- What environments can CUBA applications be deployed to?
- How to migrate a legacy solution to CUBA?
- What is the licensing of the platform and its development tools?
What is CUBA Platform?
CUBA Platform is an open-source framework intended to streamline the development process of business applications. Such applications will often require complex data models, tens or hundreds of screens, support for running various business processes, strong security requirements and so on.
So, how is CUBA Platform different from tools and frameworks already available out there? The main differentiator is that it is a high-level framework. We've created CUBA on top of the existing stable and battle-proven frameworks and added extra APIs and powerful tools to simplify development. This means that CUBA abstracts developers from underlying technologies — instead of doing routine work using generic frameworks they can focus on the business tasks, empowered by a rich set of built-in features and development tools. At the same time, CUBA does not restrict access to the underlying frameworks, providing the confidence that the resulting application satisfies all the requirements.
What’s under the hood?
CUBA framework is based on Spring Boot. So, CUBA-based applications inherit all the power of probably the richest ecosystem for enterprise-grade applications.
One of the cornerstones of the framework is metadata — the knowledge of the application data model. All components of CUBA are data-aware. They know everything they need to provide powerful features over the data model: security subsystem, both backoffice and frontend UI, generic REST API, BPM, reporting subsystem and many more other additional modules.
The persistence layer is built over well-known JPA. EclipseLink acts as an ORM framework, as it enables provident data load capabilities. Unlike Hibernate, EclipseLink has a feature of partial load not only for associations fields but also for basic attributes. CUBA introduces DataManager, which is effectively an extension for EntityManager, that applies security permissions and restrictions, enables soft deletion, audit and other useful features targeted to effective and secured data access.
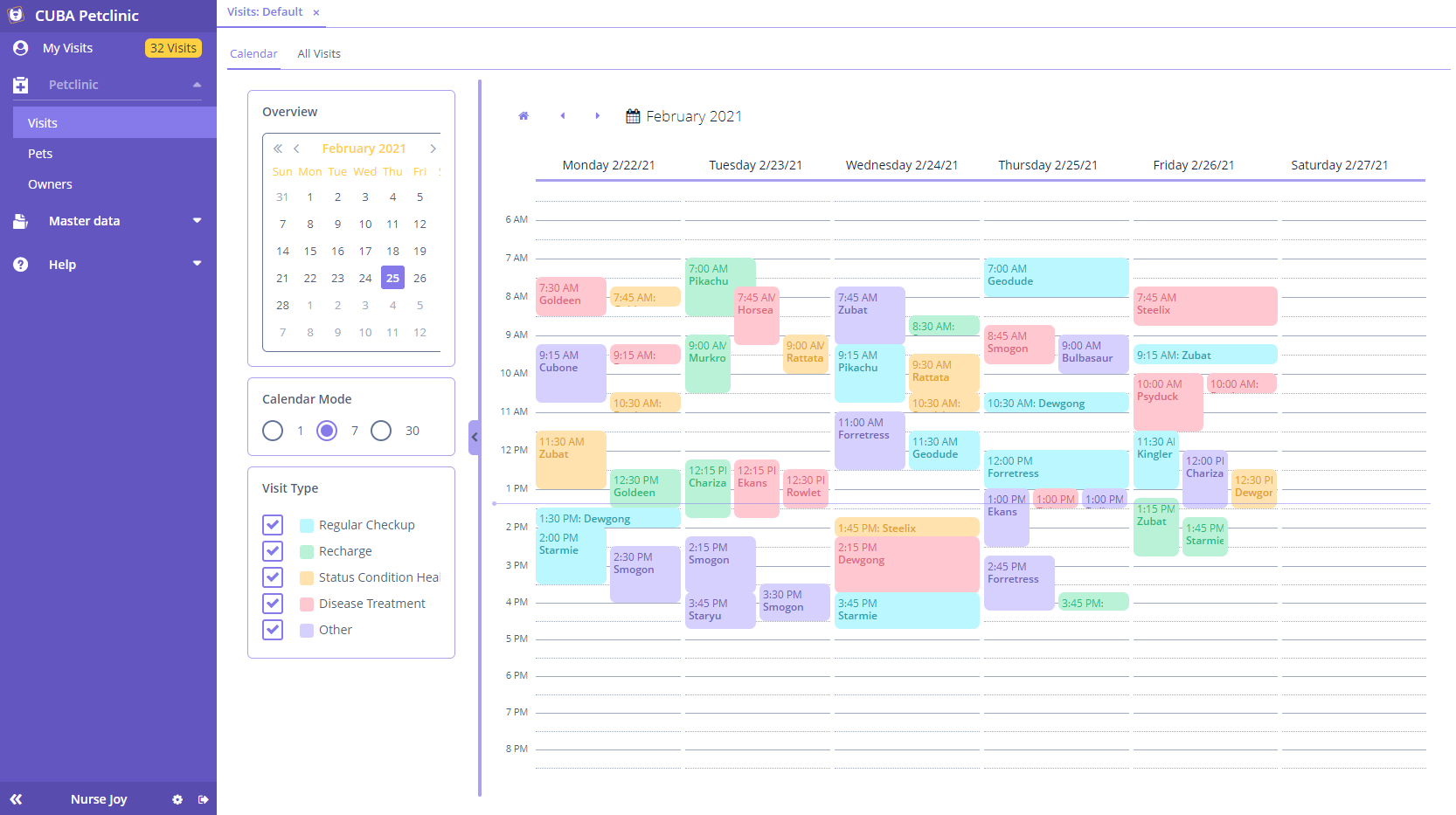
A very important part of the framework is its backoffice UI library. It provides a rich set of data-aware visual components. So, for instance, a table knows it is displaying certain attributes of a driver entity, and a label knows that it is displaying a date. Metadata helps visual components to talk to the data layer via the persistence layer — defining the graph of objects which should be uploaded or updated. This module requires no specific frontend skills for a backend developer — all UI code is written in Java and XML. The built-in component-based UI is declarative: you define screens layout in a visual editor or XML file choosing from the rich set of visual components ranging from all sorts of buttons to Google Maps and dynamic charts. Then you add the initialization and event handling logic in Java controllers. Considering data-aware components, you can create a sophisticated UI very quickly and it will remain easy to maintain, thanks to the clear separation between code and layout. If the choice of available components is not enough, there is a facility to integrate external components and writing your own component is always an option.
Backoffice UI is an ideal choice for intranet applications and administrative UIs. However, its natural limitations do not allow to develop fancy client-facing frontends. In response to the modern requirements for the user interface, CUBA provides the Frontend UI module, based on ReactJS. CUBA Studio generates TypeScript SDK generator and React code for the typical set of screens. The SDK provides both data model and application’s service calls that can be used in the front-end codebase.
All user actions are controlled by the security subsystem which is an integral part of the CUBA Platform. The role-based model controls CRUD access down to entity attributes, and even certain screen components or custom tokens that you can use in your code. Row-level security helps to control access to certain data records — for example, users from a regional department will only see documents created by this department. The security settings can be hardcoded in the application or configured at runtime in the UI of your application, so all changes can be done by system administrators on the fly.
In addition to the above, CUBA provides many features. They are either shipped with the framework or can be installed from the marketplace as an add-on. The list of features includes (but not limited to):
- User management and administration tools
- Report management
- Business process management with an integrated visual designer
- Multilanguage interface and multiple timezones support
- Full-text search
- Generic REST API
- LDAP Integration
Where can I deploy my application?
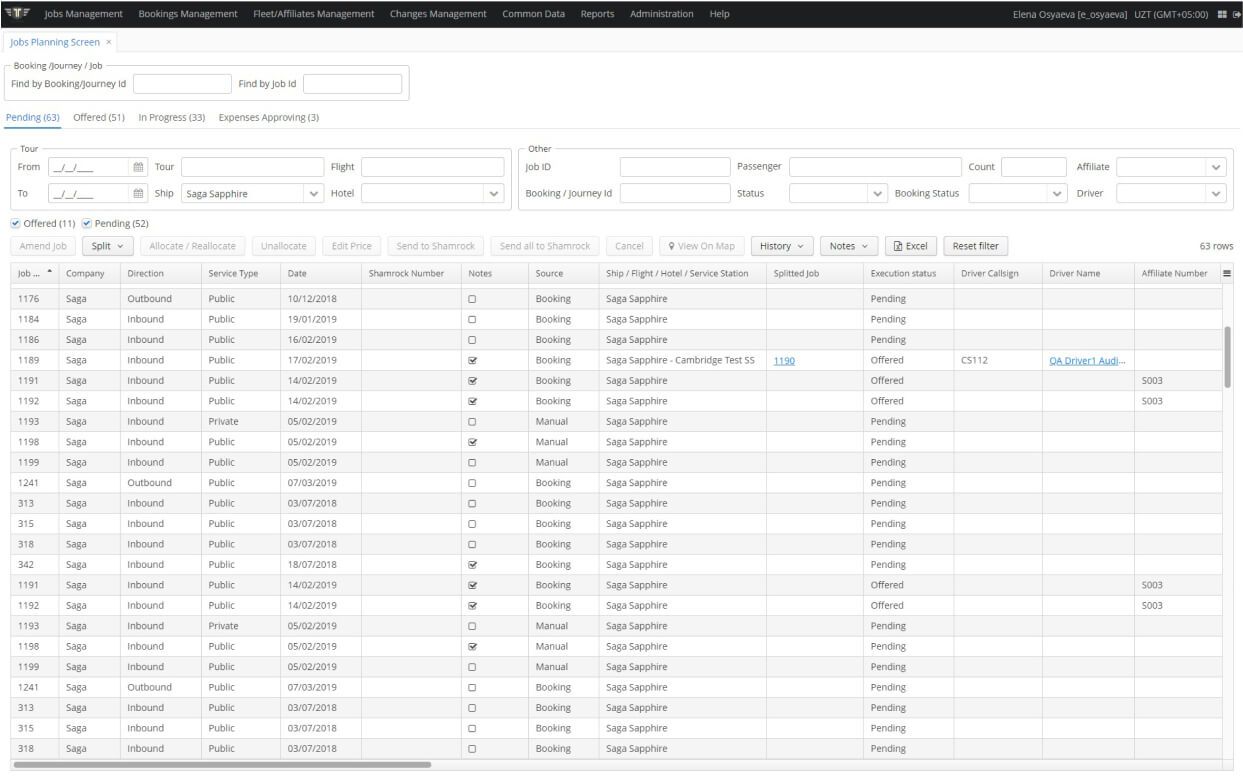
When it comes to the deployment stage and environment options, you have a lot of freedom here. CUBA applications can be deployed in a variety of configurations, starting from a single server running everything, to a highly-available clustered configuration. The platform supports PostgreSQL, Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL and HSQL (typically used for prototyping) out of the box, and you can switch from one to another as your project grows. It is also important that CUBA applications can be deployed to any Java EE Web Profile server, such as Jetty, Tomcat or Glassfish. Of course, you can encapsulate your application in Docker and/or run it in popular PaaS clouds like Amazon, CloudFoundry, OpenShift or Jelastic.
Sounds good, so how do I develop CUBA applications?
All you need to develop applications with CUBA Platform is Java SE — which makes your application code more uniform and easier to maintain. This also makes your development team more flexible — you even may not need a subteam of front-end developers or Java EE gurus.
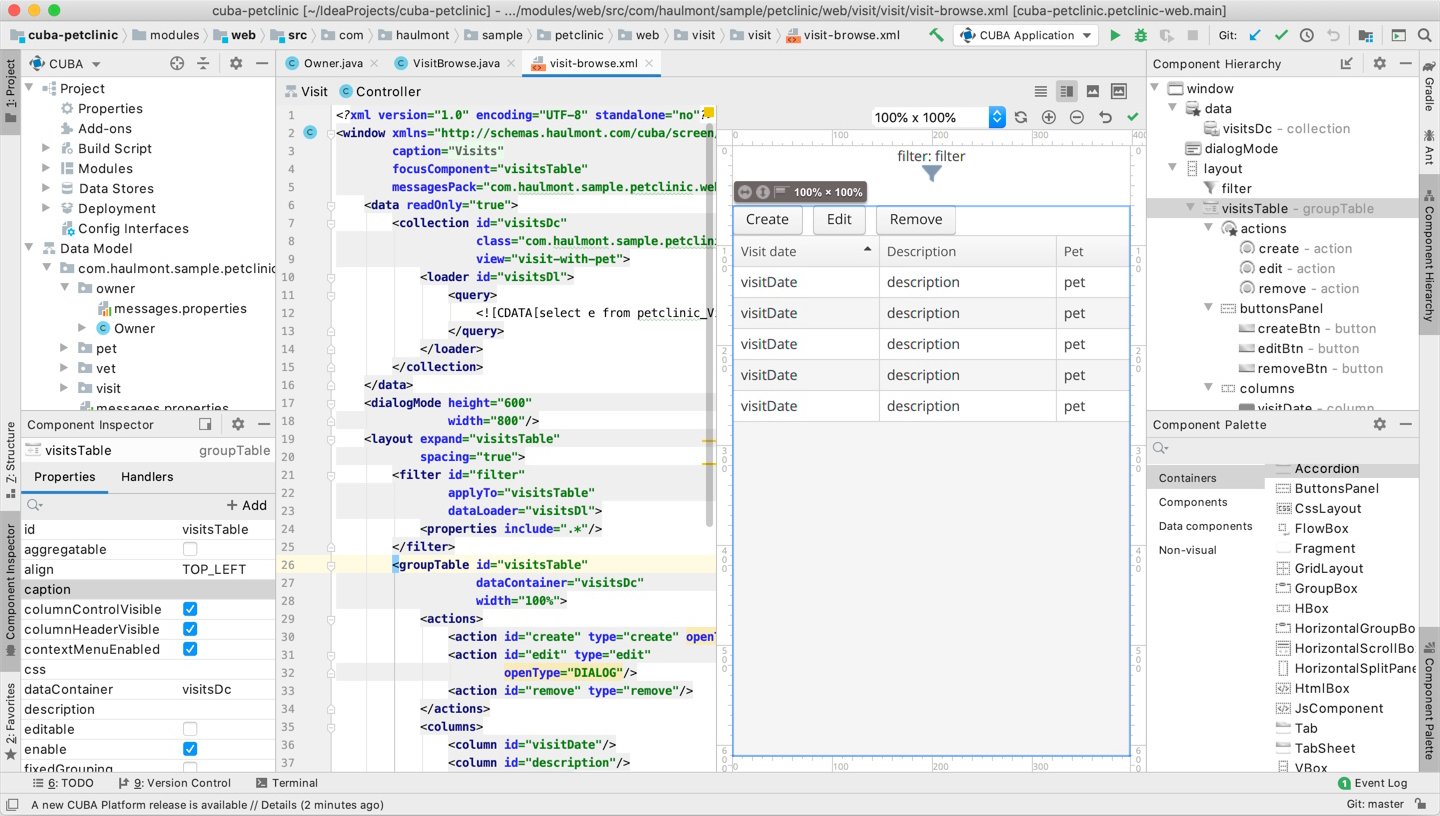
For development, you can use CUBA Studio - it's an IDE based on IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition, also available as an IDEA plugin. CUBA Studio provides the following functionality:
- enables the visual design of UI and data model
- scaffolds CRUD screens with multiple layout options
- keeps DB up-to-date by automatically generating and running update scripts
- generates stubs for event handlers, services, etc.
The Studio utilizes IDEA's project metamodel, therefore supports code completion as well as component and services injection and many other coding assistance features throughout project's codebase. To boost development productivity even further, the Studio automatically hot deploys all your code except for the data model. Thus, it eliminates a lot of routine work.
If you think of upgrading your legacy system to a modern Java stack, CUBA has an answer for this too. The studio features a migration tool, which will convert a legacy database to CUBA-compliant and automatically generate screens based on the DB schema. Thus you will only need to add custom screens and migrate business logic.
OK I’m almost convinced... what about licensing?
As stated in the title, the core framework is open source, licensed under Apache 2.0 with its source code available on GitHub. This means that there are no license limitations on the software you develop using CUBA Platform.
CUBA Studio is also free, excluding the following features that are available via commercial subscription:
- visual data model designer
- WYSIWYG screen designer
- visual UI theme editor
Other than these visual editors, there are no limitations in the free version of the Studio. The price of annual per developer subscription starts from just $189 p.a. Even if your subscription is expired, the Studio will remain fully functional and you can continue working with the project codebase.
Hopefully, this overview gives you a good idea of what CUBA Platform is and makes it tempting to try. If so, simply go to the website, download Studio, pass the Quick Start and have your first CUBA application running in a matter of minutes!