What is Rapid Application Development
Rapid application development (RAD) is a development approach focusing on designing and prototyping stage for the purpose of getting instant user feedback. Unlike traditional development models with initial planning and further execution RAD implies more flexibility. Constant iterations of user feedback and quick incremental updates help to achieve better result at the end of the day.
James Martin defined what is rapid application development in 1991 as an alternative to the rigid waterfall processes. The classic waterfall approach works perfectly in construction and many other industries where scope changes are rare and expensive. If you started building a bridge, it is unlikely that you would swap it for a ferry halfway through the process.
Software development is much more flexible. There are more variations of how the same business challenge can be resolved, and at the same time changes are cheaper. As a result, super-detailed design and planning often lose out to the trial and error approach. Moreover, users tend to provide better feedback only when they see something working.

Requirements planning
DESIGN
User design
User design is the crucial part of the rapid application development methodology distinguishing it from the classic waterfall model. Here, developers start with working on a prototype. The goal is to demonstrate something to the client as soon and as cheap as possible. It is acceptable that the prototype only satisfies part of the requirements or covers only certain scenarios. It is acceptable to cut corners at the code level.
After the prototype is ready, it is presented to the users. The team collects all possible feedback and this is where initial requirements are subject to inevitable changes. Something which seemed right on paper may look totally different in a working application. With this feedback at hand, developers return to the prototyping step, until users are satisfied with the result.
Construction
Now we know exactly what needs to be done. It is time to develop and test the system so that it is ready for production use. No more cutting corners, the focus is on quality, scalability, maintainability, etc. However, users continue to participate even at this late stage, providing feedback as features get implemented. A bit of fine tuning is still possible on this stage of the rapid application development cycle.
What we have developed at the prototype stage might even be thrown in a bin, depending on the tool we chose and other circumstances.
Cutover
This is the final phase including acceptance testing, rollout and user training.
Rapid Application Development vs. Agile
The RAD term predates Agile by 10 years, and for its iterative approach it is often considered a “parent” of Agile. However, this is not the case. While RAD is a prescriptive development methodology, Agile is a philosophical position, encompassing much more than just development.
It would be fair to say that RAD belongs to the family of agile software development methodologies, together with Scrum, Kanban and many others.
Is Rapid Application Development applicable to my project?
- the budget and timeframes have to be known in advance.
- you do not have regular access to the users or they are not motivated to commit their time and energy
- the project requires a large team due to its scale, or an excessive amount of stakeholders
These conditions are often true for large business or governmental organizations. However, certain elements of rapid application development methodology can be applied even in such cases. E.g. fixed price projects can budget for prototype stage and certain amount of changes. Prototype scope could be limited to the most uncertain parts, considering that you have relevant users on board.
On the other side, rapid application development framework works very well for small and medium businesses, or departmental projects, where business users own the budget and are motivated to get the results. A classic example is various Line-of-Business (LOB) applications - a general term describing applications developed to automate and run certain parts of business more efficiently.
Similarly, RAD is perfectly applicable to creating websites. These are typically small projects with a limited set of stakeholders, but involving them early is crucial as design is a very opinionated thing, and everyone will have something to say!
Rapid Application Development Tools
Design and Prototyping
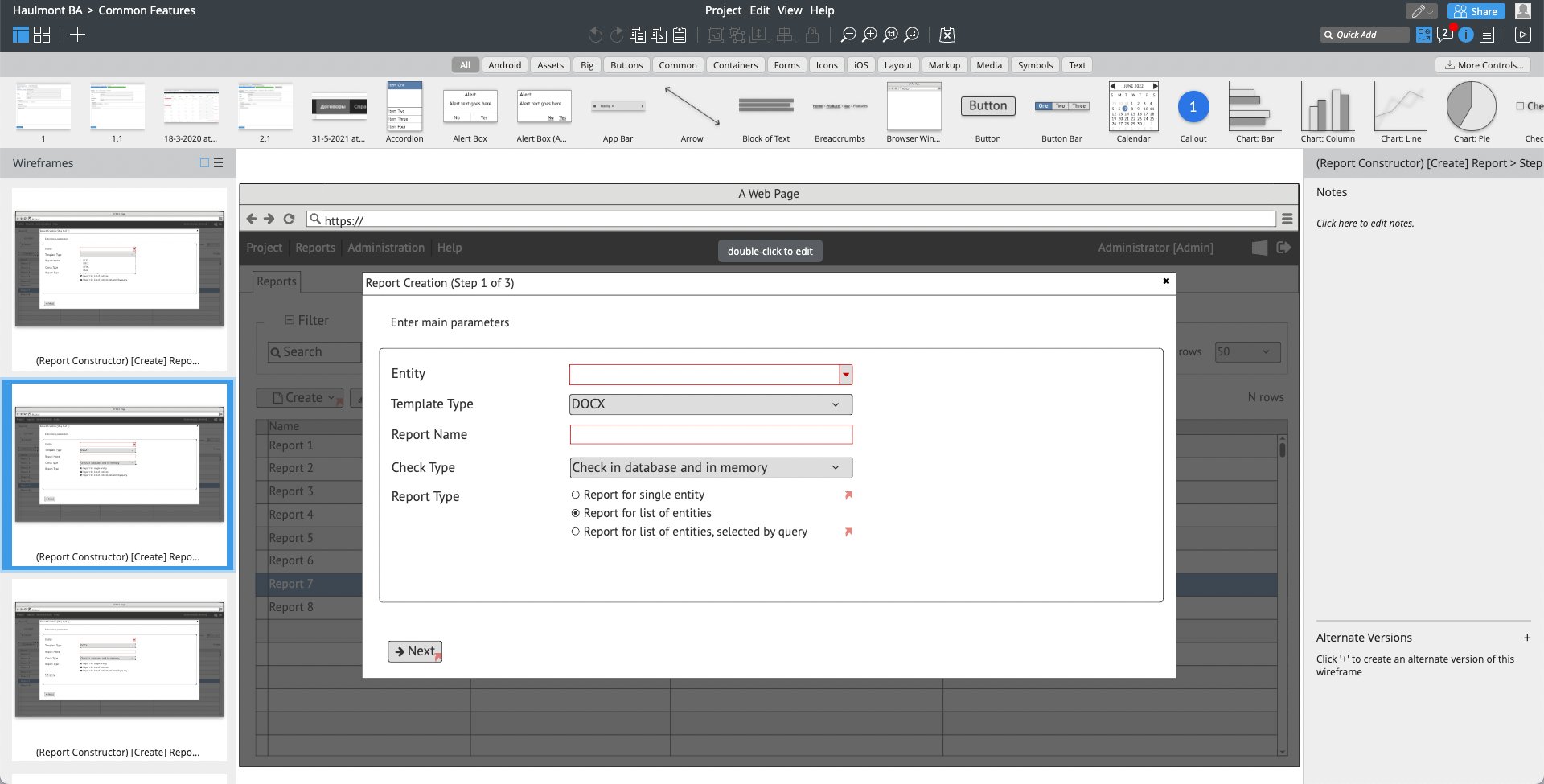
Development
Development is usually by far the most time consuming, expensive and uncertain part of creating an application. So, modern rapid application development platforms combine proven architecture, ready components implementing typical features, and of course tools facilitating rapid development. All of them help you deliver results quicker both at the Prototyping phase of the project and further during Construction.
Consulting firms like Gartner and Forrester keep introducing new terminology to distinguish between these platforms: Low/No Code Application Platforms (LCAP), High Productivity Application Platforms as a Service (HPAPaaS), Multi Experience Development Platforms (MXDP). However, ultimately all of them can be classified by their target audience.
Low Code / No Code Platforms

Developer-focused platforms
These platforms leverage the speed and joy of software development mostly by providing higher-level API and code generation - so developers are kept away from repeating boilerplate code and typical functionality.
Embarcadero RAD Studio, previously known as Borland Delphi, is one of the pioneers in this space, famous for its visual UI designer. It appeared before the web era and is still applicable only for desktop and mobile applications.
Other rapid application development frameworks focus on the web as it is a dominant channel for interaction with end-users these days. For example, at Jmix we try to join the convenience and speed of visual data model and interface design with the power of modern open source technologies. Such approach not only boosts prototyping speed, but also enables you to grow your prototype into a full-featured enterprise application with a solid and scalable architecture. You can get a feel of how it works in several minutes by watching a 7-minute overview video.
Summary
Rapid Application Development is one of the development methodologies following the agile philosophy. The key principle of RAD is a close engagement of end users and fast, iterative prototyping based on user feedback. When the users are happy, the focus is shifted to the delivery of production-ready software.
Choosing the right tool(s) is critical to ensure fast prototyping and thus the successful implementation of RAD methodology in a project. Luckily, there is a wide choice of tools and platforms aimed at different types of applications, stages of a project and team skillset.
RAD is an old concept, but today it is experiencing a renaissance following the trends of digital transformation and the push towards faster time to market. For the right types of projects and team setup, RAD methodology helps to achieve better user satisfaction with reduced risks and in shorter timeframes.
Related articles